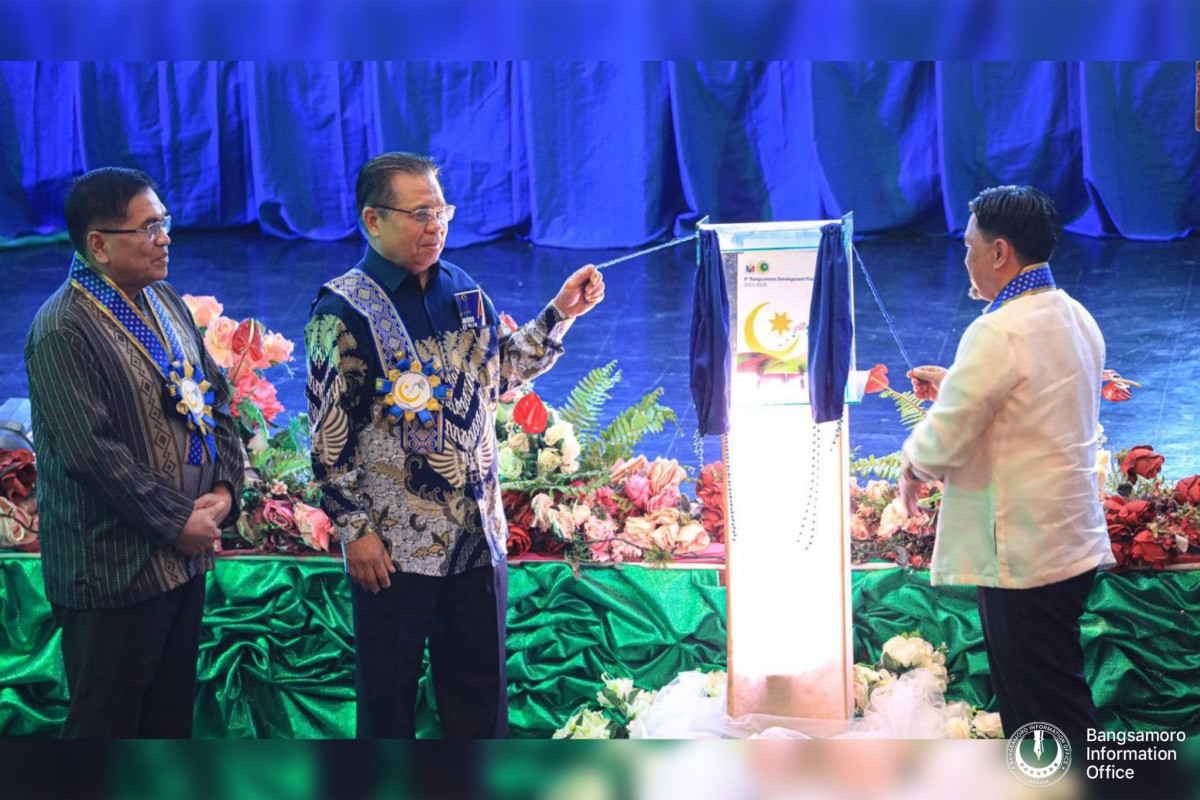
PIA COTABATO CITY -- In a bid to provide a roadmap that outlines the region’s development priorities in the next six years, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) government recently launched in Cotabato City its second Bangsamoro Development Plan (BDP), marking another huge milestone for the Bangsamoro government.
Composed of 14 chapters, the BARMM’s second BDP serves as a guidepost that underscores the development thrusts, priorities, and strategic directions of the Bangsamoro government for the years 2023 to 2028.
The said plan was also carefully crafted to sustain the gains achieved by the BARMM government for the past three years as outlined in the first BDP 2020-2022.
“This plan is a major accomplishment for every Bangsamoro, as it sets the development thrusts, priorities, and strategies of the government for a 6-year period from 2023-2028,” BARMM Chief Minister Ahod Murad Ebrahim said.
He added that the dreams and aspirations of the Bangsamoro people cannot be realized unless everyone will work together and decides to achieve the aspirations of the Bangsamoro people.

The six years BDP was crafted in support of the Enhanced 12-Point Priority Agenda of the BARMM. It is also anchored on the Mindanao Development Plans, the 8-point Socio economic Agenda of President Ferdinand Marcos, Jr., the Philippine Development Plan 2023-2028, and the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals.
Moreover, among the most notable macroeconomic goals of the 2nd BDP which the BARMM government is expected to achieve at the end of the 6-year plan include the following: Eight percent to 9 percent Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP) annual average growth rate; 6 percent to 9 percent GRDP annual per capita-annual average growth rate; 10 percent to 12 percent annual double-digit real growth of industry and services sectors; 18 to 20 Gross Capital Formation (GCF) as a percentage of GRDE/GRDP; 2 percent to 4 percent inflation rate; 3 percent to 5 percent unemployment rate; 4 percent to 7 percent underemployment rate; and 20 percent to 25 percent poverty incidence.
Meanwhile, Republic Act No. 11054, known as the “Bangsamoro Organic Law," serves as the policy framework for crafting the 1st and 2nd BDP.
Aside from this law and the moral governance principle which serve as a guide for leadership and service delivery in the BARMM region, the 2nd BDP is also guided by three cross-cutting themes: "Inclusion, Equality, and Justice."
The formulation and packaging of the 2nd BDP were in partnership with BARMM’s development partners, such as the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), The Asia Foundation (TAF) through Forward Bangsamoro, the European Union through the Support to Bangsamoro Transition (SUBATRA), United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (UNFAO), International Labour Organization (ILO), United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), and the International Organization for Migration (IOM). (With reports from Bangsamoro Government/PIA-XII)